The Last Mile Delivery market is expected to grow significantly with various trends according to various market researches. It is expected to grow from $202.01 billion in 2025 to $324.48 billion in 2029 [1]. Same day delivery, Automation, Electric Vehicles and Green Logistics are some of the market trends [2]. OPEVA contributes these within “Demo 5: Energy Efficient Route Planning for Mil Delivery” as follow:
Route Optimization for Last Mile Delivery
Logistic providers and e-commerce retailers have seen that customer expectations in last mile delivery have changed especially in the last decade and have endeavored to produce solutions accordingly. In e-commerce, customers now expect options such as “same day delivery” or “next day delivery” as well as the ability to choose a specific delivery window. OPEVA proposes route optimization and delivery scheduling of electric vehicles in last mile delivery tasks [3]. The proposed solutions are tested both on benchmark problems [4], and in Eskişehir Osmangazi University (ESOGU) Campus (see Figure 1).
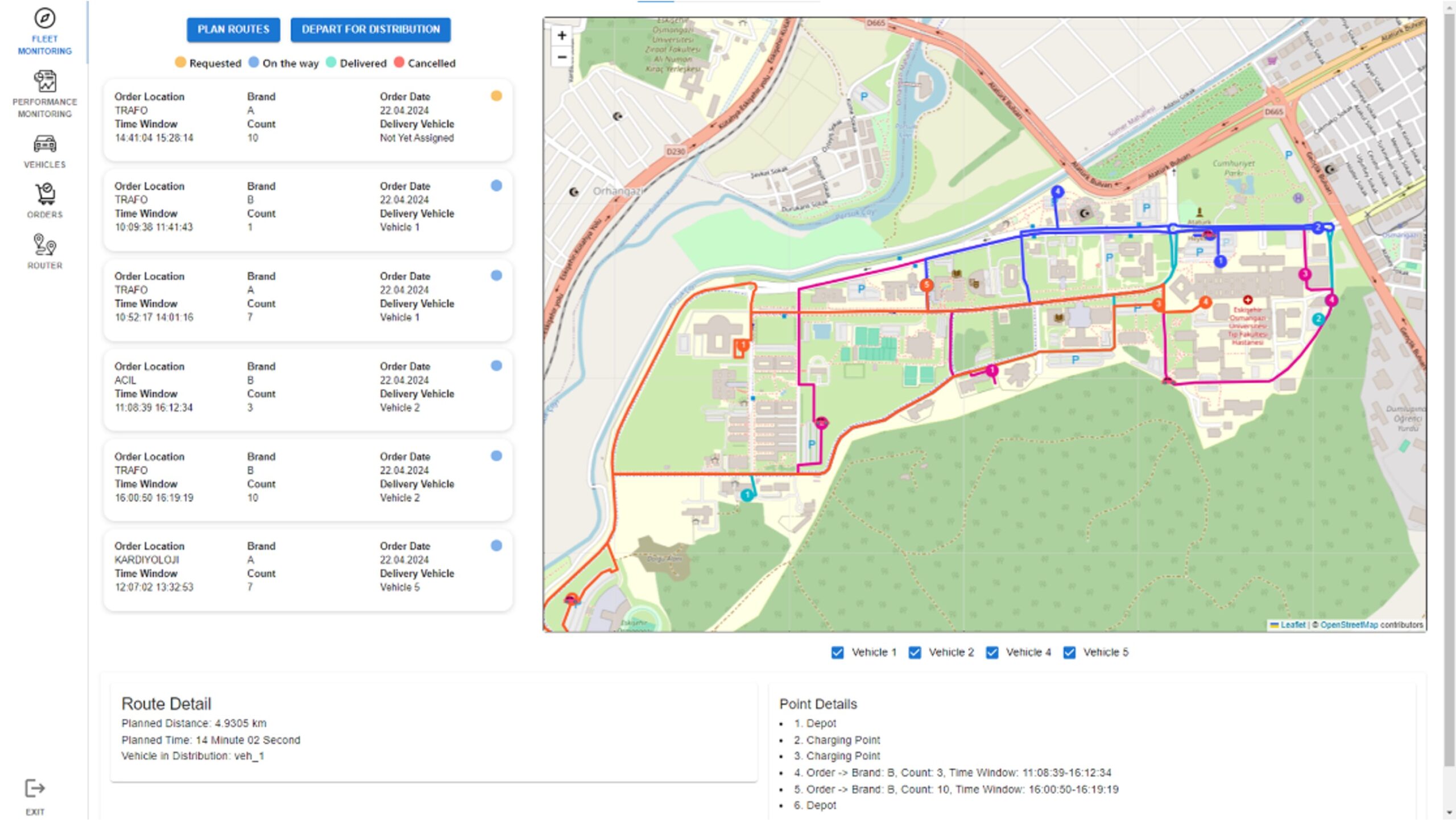
Figure 1. ESOGU Test Environment for Last Mile Delivery.
The task of logistics providers now requires leveraging data analytics for route optimization and investing in automation. The inclusion of sustainable delivery options that appeal to environmentally conscious consumers has also been an important competitive element in recent years.
EVs & Green logistics
As environmental concerns grow, businesses’ responsibility to ensure sustainability is becoming increasingly important. The rising global awareness of ecological responsibilities makes it essential to adopt new approaches in traditional logistics processes, particularly in transport, storage, and packaging, which often have significant environmental impacts. In this context, green logistics—encompassing environmentally friendly practices in supply chain management and logistics—has gained prominence.
One key initiative is the shift to electric vehicles (EVs) for urban deliveries, replacing conventional fossil fuel-powered vehicles. The OPEVA project focuses on integrating lightweight EVs into last-mile delivery operations, with an emphasis on L5 category EVs, as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2. The L5 MUSOSHI Electric Vehicle
Within the scope of the OPEVA project, the use of L5 category EVs in last-mile deliveries is demonstrated. Studies on the remaining range and energy consumption estimation in EVs have enabled the determination of energy-efficient routes.
Fleet management for EVs
Customers want to track their deliveries in real time. This requires the development of advanced tracking technologies. Customer expectations in last mile delivery, such as delivery speed, real-time tracking, convenient delivery times, accurate delivery time estimates, low-cost or free delivery, flexible delivery options, environmentally friendly delivery options, emerge as important competitive elements for logistics providers. Even if the delivery is handled by a third-party logistics provider or local delivery service, the brand or retailer which customers purchase from will be impacted by the experience. OPEVA realizes both vehicle tracking and orders status tracking (See Figure 3).
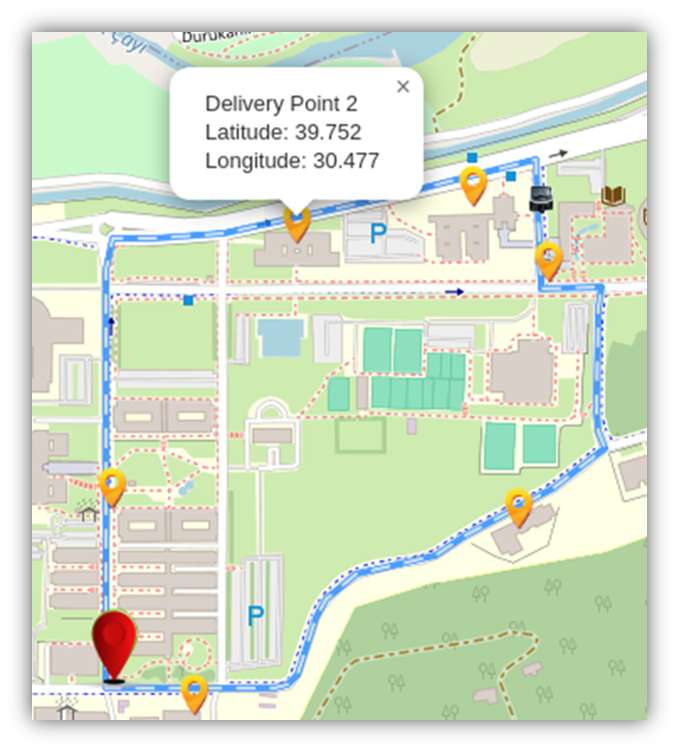
Figure 3. OPEVA Vehicle Tracking
On the other hand, Prognostic Health Management (PHM) plays a critical role in ensuring the efficiency and sustainability of last-mile delivery operations, particularly with the growing reliance on EVs. By leveraging advanced data-driven methodologies, PHM enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of delivery fleets, ensuring vehicles remain operational with minimal disruptions. Tools like machine learning models and real-time diagnostics help predict the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of critical EV components, such as batteries and electric drive systems, reducing unexpected failures.
In the OPEVA project, Prognostic Health Management (PHM) is designed to improve the reliability and longevity of electric vehicles (EVs) used in last-mile delivery. Using a data-driven PHM tool (KT14), it aims to optimize battery management, reduce maintenance time, and extend vehicle lifespan through advanced predictive insights. The tool enhances the accuracy of key predictions, such as state of charge (SoC) and state of health (SoH), by enabling real-time monitoring of critical battery parameters. Additionally, it provides valuable forecasts to support vehicle longevity and overall fleet efficiency.
Autonomous Delivery Solutions in Last Mile Delivery
In the OPEVA project, LOXO represents a groundbreaking step towards establishing Europe’s first commercial autonomous delivery service at the scale of a whole city. By seamlessly combining LOXO’s advanced autonomous vehicle technology with its logistic partner extensive logistics expertise, the project redefines last- and middle-mile delivery processes (See Figure 4). Through the OPEVA project, the necessary groundwork, including data collection, simulation, and the training of the LOXOFuser—a critical element of LOXO’s autonomous driving software—will be laid. This innovative collaboration sets the stage for showcasing transformative applications within our internal projects, underscoring the potential of autonomous technology in modern logistics.
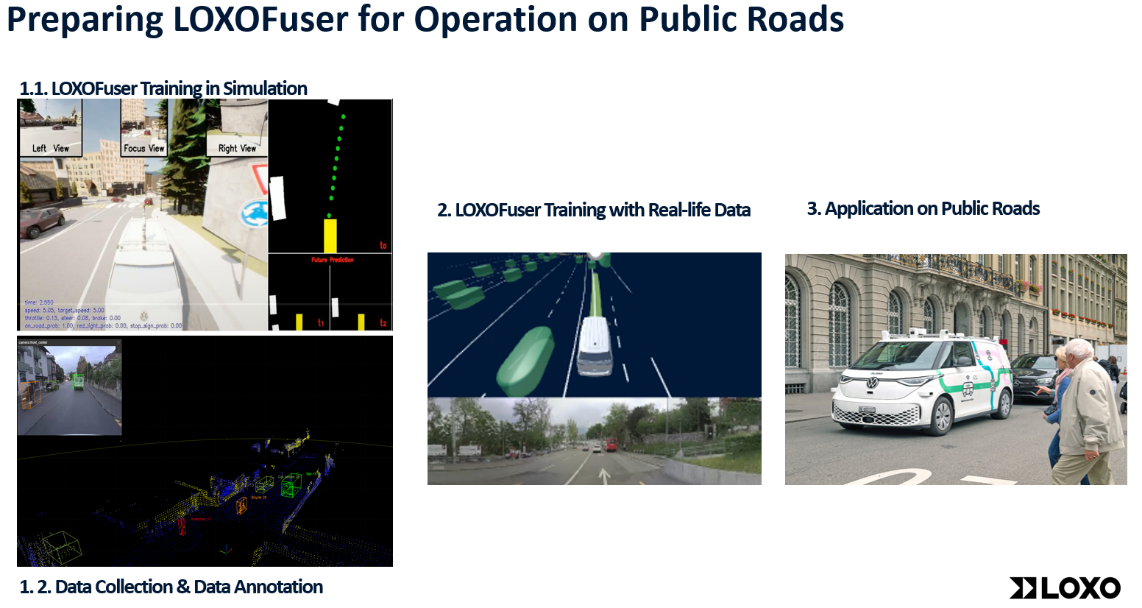
Figure 4. OPEVA Autonomous Delivery
For more information, contact:
-Ahmet Yazıcı, ayazici@ogu.edu.tr, Eskisehir Osmangazi University
– Yunus Sabri Kırca, yunussabri.kirca@ogu.edu.tr, Eskisehir Osmangazi University
-İnci Sarıçiçek, incid@ogu.edu.tr, Eskisehir Osmangazi University
-Sinem Bozkurt Keser, sbozkurt@ogu.edu.tr, Eskisehir Osmangazi University
-Kadir Berkhan Akalın, kbakalin@ogu.edu.tr, Eskisehir Osmangazi University
-Marc Gremaud, marc@loxo.ch, LOXO AG
-Okan Ulu, okan.ulu@inorobotics.com, Inovasyon Mühendislik
References:
[1] Last Mile Delivery Global Market Report 2025, The Business Research Company, Published: January 2025
[2] Last Mile Delivery Market Comprehensive Study Report with Recent Trends, Introspective Market Research, Published: December 2024.
[3] Kucukoglu, I.; Dewil, R.; Cattrysse, D. “The electric vehicle routing problem and its variations: A literature review,” Computers & Industrial Engineering, 161, 107650, 2021.
[4] Aslan Yıldız, Ö.; Sarıçiçek, ˙I.; Yazıcı, A. “A Reinforcement Learning-Based Solution for the Capacitated Electric Vehicle Routing Problem from the Last-Mile Delivery Perspective”. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031068
